Quick Start Using Docker
We have created a project you can fork and start building your own project with Docker built in. This project has the Dockerfile which provides the base PHP-FPM. It also contains the docker-compose file to make it easy to include Nginx and the project's app image.
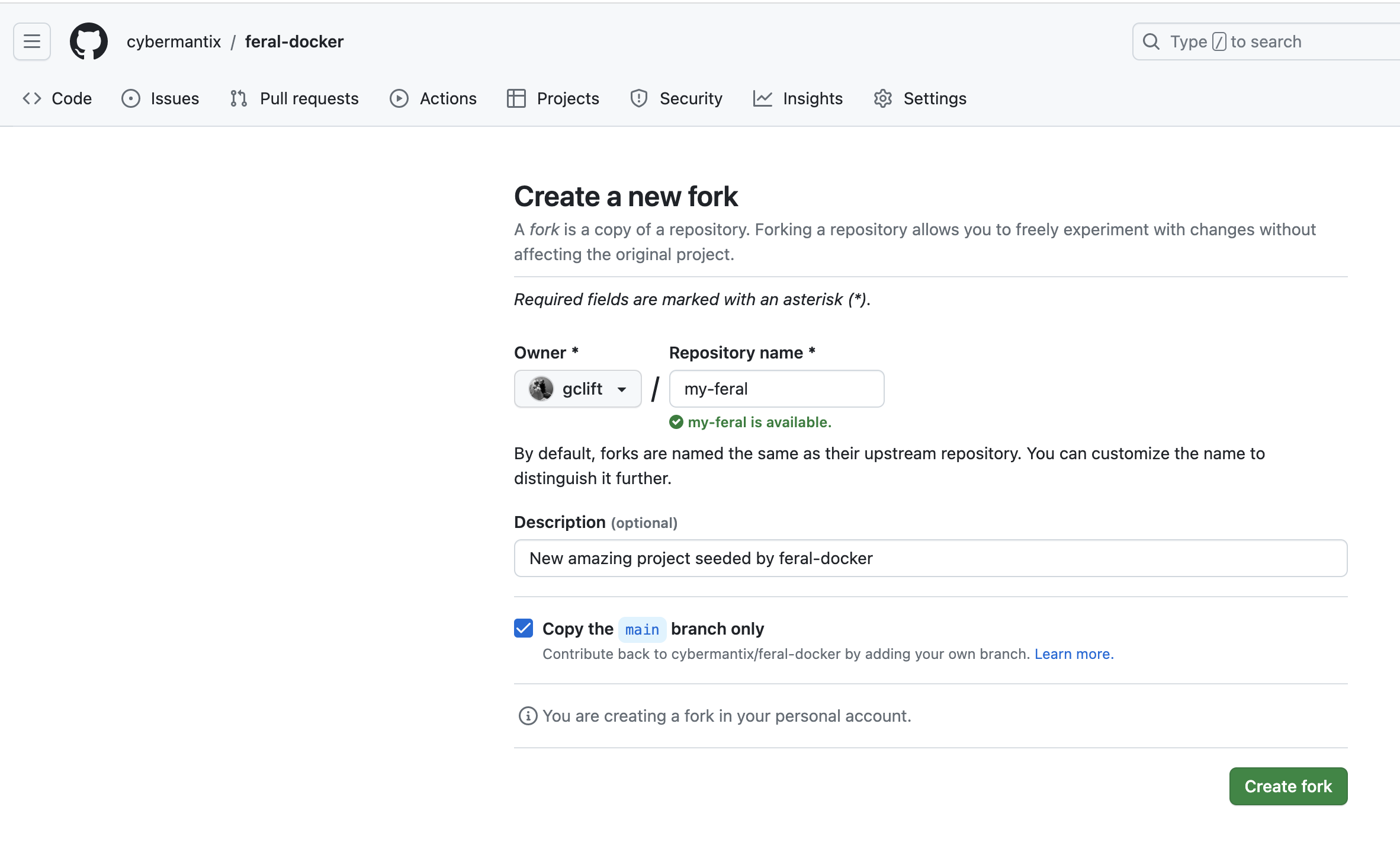
Step 1: Fork the repository
Like a good cover, say Siouxsie & The Banshees 'The Passenger', the best work is based on an established work. The first step to using the Feral Docker project as a base is to fork the repository.
- Visit https://github.com/cybermantix/feral-docker
- Click
Forkin the sub nav. - Enter the new repository and description
- Click
Create Fork
Step 2: Clone your fork locally
After you have forked the repo, you need to clone it to your development environment to start building.
git clone ssh://john@example.com/path/to/my-project.git
cd my-project
Step 3: Build the Feral Docker Image
Once you have cloned the repository locally, you'll need to build the docker image. To
build the image, you'll need to cd into the docker directory of your project and use the
Makefile target build to build the image.
This could take several minutes to build.
cd docker
make build
Step 4: Start the container and make a terminal
This tutorial will use two terminal tabs. The first will be the runner tab which you
will start the container and will continue to remain connected to the container. The
second tab is the term tab used to get a terminal in the container.
Once the Docker image is built, you can create a container with the image. Using the
start target in the Make file
# RUNNER TAB (left tab)
# from the docker directory
make start
In the current terminal window you'll see information from the docker/bin/startup script.
Once you see PHP-FPM is ready to handle connections, you can create a terminal window.
# TERM TAB (right tab)
# in a seperate terminal window or tab
# from the docker directory
make term
At this point you should have two terminal windows or tabs. You can see the output of each container in the initial window.
Step 5: Install Symfony and Feral Slack
Do this step from the Docker terminal window, in the right tab.
The Makefile contains a target install which will install symfony and the feral-inline package.
To run the install target, in the terminal window type make install.
# in the terminal window running the the term command
# from the /opt/app directory
make install
Step 6: Run Feral commands
# in the terminal window running the the term command
# from the /opt/app directory
bin/console feral:catalog
The output will show all of the CatalogNodes available in the project.
# output
Feral Catalog
CALCULATION
- Add (add) : Add two values stored in the context.
- Divide (divide) : Divide two values stored in the context.
- Multiply (multiply) : Multiply two values stored in the context.
- Power (power) : Raise the value from the x path to the power of y.
- Random (random) : Add a random value to the context
- Subtract (subtract) : Subtract two values stored in the context.
- System Random (system_random) : Add a random value to the _random context key
COMPARATOR
- Equals Zero (equals_zero) : Check if a context value is zero.
- Greater Than (greater_than) : Check if a context value is greater than a configuration value.
- Greater Than Zero (greater_than_zero) : Check if a context value is greater than zero.
- Less Than Zero (less_than_zero) : Check if a context value is less than zero.
CONTEXT
- Set Context Value (set_context_value) : Set a value in the context using a value and a path to the location.
DATA
- Counter (counter) : A counter that ticks every time the node is processed.
FLOW
- Start Processing (start) : The start node will start a process and return an OK result.
- Stop Processing (stop) : The stop node will end a process.
- Throw Exception (throw) : Throw an exception.
LOG
- Debug Logger (log_debug) : Log a message with the debug level
- Error Logger (log_error) : Log a message with the error level
- Info Logger (log_info) : Log a message with the info level
- Notice Logger (log_notice) : Log a message with the notice level
- Warning Logger (log_warning) : Log a message with the warning level